Flow of genetic information from DNA to DNA - Replication of DNA
- Francis Crick proposed the process of central dogma in molecular biology.
- According to this, the flow of genetic information takes place from DNA to DNA rather than mRNA and protein.
- The flow of genetic information from DNA to DNA is called replication. And from DNA to mRNA is called transcription.
- Whereas from mRNA to protein is called Translation.
- The process of flow of genetic information from DNA to DNA is known as Replication. During this process, Genetic information is copied from parental DNA to DNA of offspring.
- Replication occur at S phase of cell cycle in nucleus in Eukaryotic but in cytoplasm of prokaryotic cell.
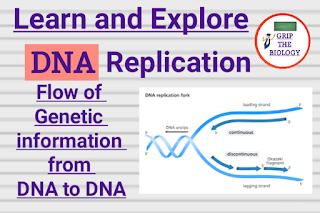
- During replication,Both strands of DNA strand are opened with the help of helicase enzyme and single strand binding protein. This is also called unwinding of DNA helix.
- To avoid the coiling of DNA strand, topoisomerase enzyme may be used.
👌👌Remember - Opening of DNA Helix is a high energy process therefore DNA helix is not opened completely, it always opens up to half its length.
- After the unwinding of DNA helix by the action of helicase enzyme, it assume a Y shaped structure called replication fork.
- The position at DNA helix from where opening occurs called origin of repliication or ori.
- On the strand of DNA with polarity 3' to 5' a piece of Primer is formed at three prime end.
- This primer is made up of RNA polymerase.This RNA polymerase does not take part in process of replication.
- This primer is extended according to nucleotides present on strand of DNA with polarity from three prime to five prime.
- This extension of primer occurs due to. polymerisation of nucleotides. This extension or polymerisation of nucleotides takes place by DNA polymerase enzymes.
- DNA Polymerase is highly efficient enzyme and it can polymerised 2000 base pair at every second.
- The extension of primer on strands of DNA with three prime to five prime polarity occurs in continuous manner therefore this strand is known as continuous strand or leading strand.
- The extension of the primer on strands of DNA with five prime to three prime polarity occurs in discontinuous manner or the primer extends in the form of fragments.
- These fragments are called Okazaki fragments and this strand is known as discontinuous strand or lagging strand. Later on these fragments are joined by the ligase enzymes.
- At last, proofreading of strands is done by the DNA Polymerase third enzyme. During proofreading mismatching nucleotides on newly formed strands on DNA are removed.
- In this way two molecules of DNA are formed from a single DNA molecule through DNA replication or DNA Duplication.
- The process of DNA replication is semiconservative in nature because in a newly formed DNA molecule one strand is old and another strand is new.
- Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate serve as dual purpose during replication . It act as source of energy and act as substrate for the polymerisation of nucleotides.
Comments
Post a Comment